EV Truck Drive Systems: Comparing Direct Motor and E-Axle Technologies
The Global Shift Toward Low-Carbon Transportation
As businesses around the world intensify their efforts to reduce carbon emissions, many are increasingly investing in electric and hybrid vehicles. The transition to sustainable transportation is not only driven by environmental concerns but also by regulatory pressures, fuel cost savings, and advancements in electric vehicle (EV) technology. While some companies are opting for fully electric vehicles (EVs) that rely entirely on battery power, others are incorporating hybrid solutions that blend conventional internal combustion engines with electric components to decrease dependence on fossil fuels.
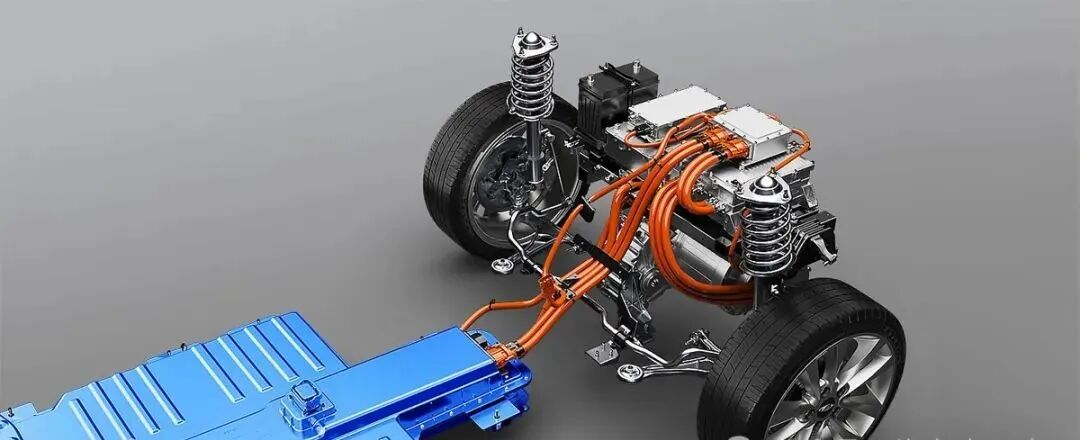
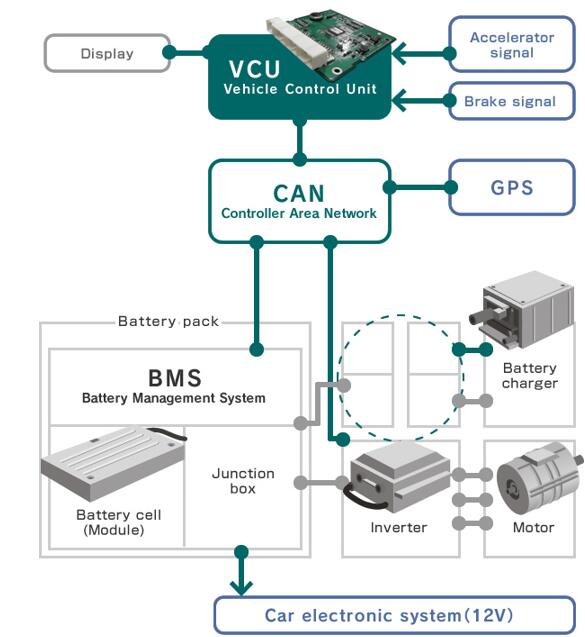
One significant innovation facilitating this transition is the electric axle (ev Axle)—a technology that integrates electric propulsion into a vehicle’s drivetrain, making it more energy-efficient and environmentally friendly. By electrifying all or part of a vehicle’s powertrain—the system responsible for converting fuel or electricity into motion—companies and individuals can take a significant step toward achieving lower-carbon transportation.
This article explores ev Axle technology, its benefits, how it works, and what the future holds for this critical component in the evolution of electric and hybrid vehicles.
 Matching vehicle type tractor2.png)
The Role of Electrification in Modern Transportation
Engineering advancements have enabled the electrification of many modes of transportation, reducing reliance on carbon-intensive fuels. In the past, fully electric vehicles (EVs) were considered impractical for commercial applications due to limited range, high costs, and inadequate charging infrastructure. However, today’s EVs have made significant strides in performance, range, and cargo capacity, making them viable alternatives to traditional diesel-powered vehicles.
A growing number of businesses have successfully integrated EVs into their fleets, particularly for last-mile deliveries, where shorter distances and frequent stops make EVs an ideal choice. However, many companies are still evaluating the economic and logistical feasibility of using EVs for long-haul transportation and heavy-duty freight applications.
While EV charging infrastructure is improving, it remains insufficient to support large-scale electrification of commercial vehicle fleets. For instance, a study projects that by 2035, truck stops equipped to charge electric trucks will require as much power as a small town. Even for advanced electric semi-trucks capable of traveling up to 500 miles on a single charge, such as Tesla’s electric semi-truck, high purchase costs remain a significant barrier for businesses with limited budgets.
To address these challenges, many companies are turning to hybrid solutions, which combine conventional and electric propulsion technologies. Hybrid vehicles offer a more affordable and practical alternative, bridging the gap between fossil-fueled and fully electric vehicles. A key enabler of this transition is the ev Axle, which plays a pivotal role in both hybrid and fully electric vehicle designs.
What is an ev Axle?
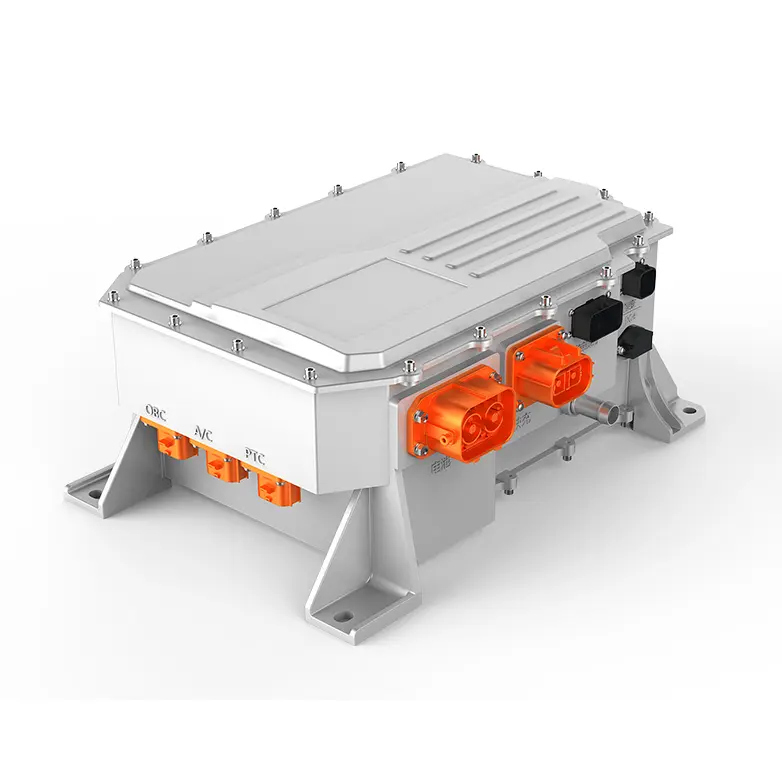
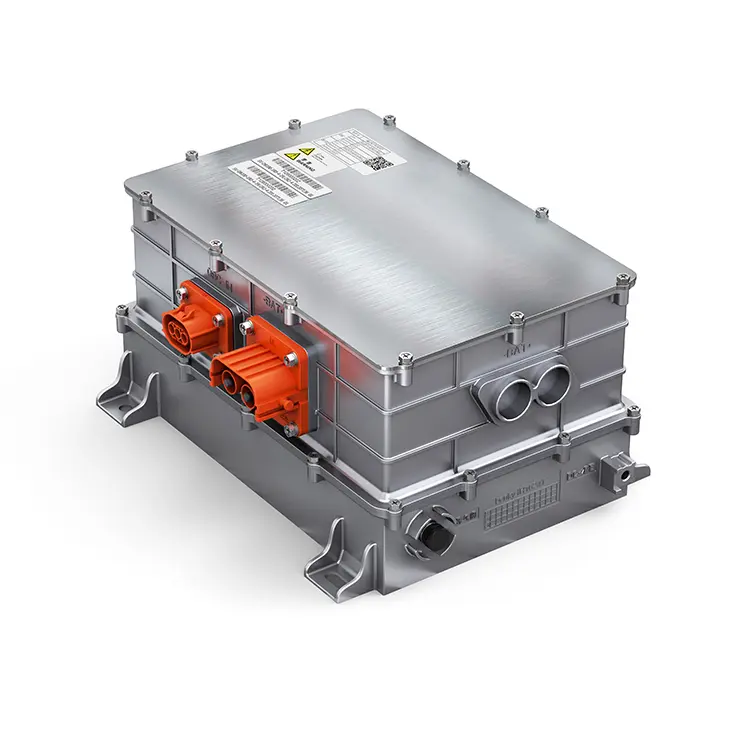
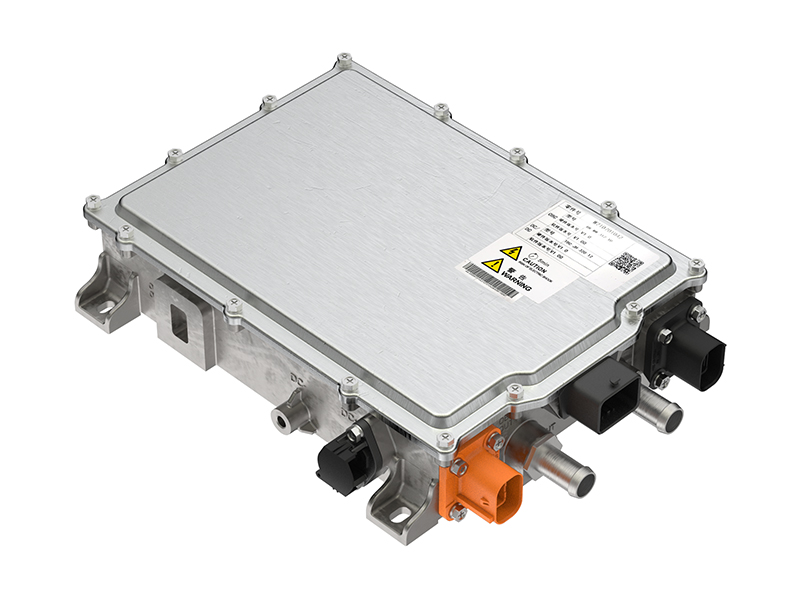
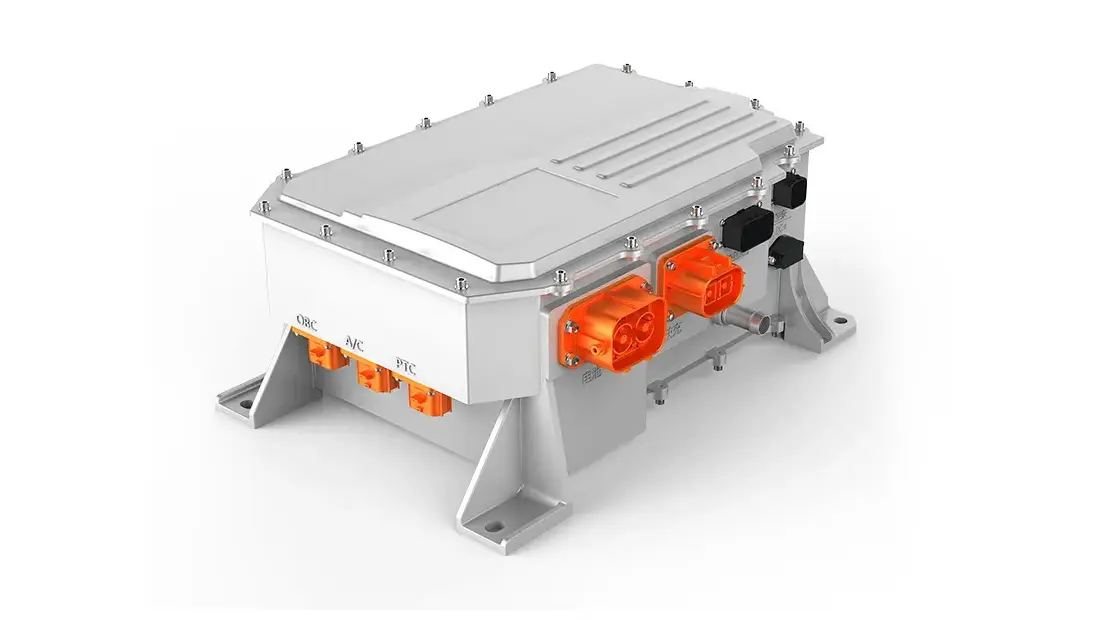
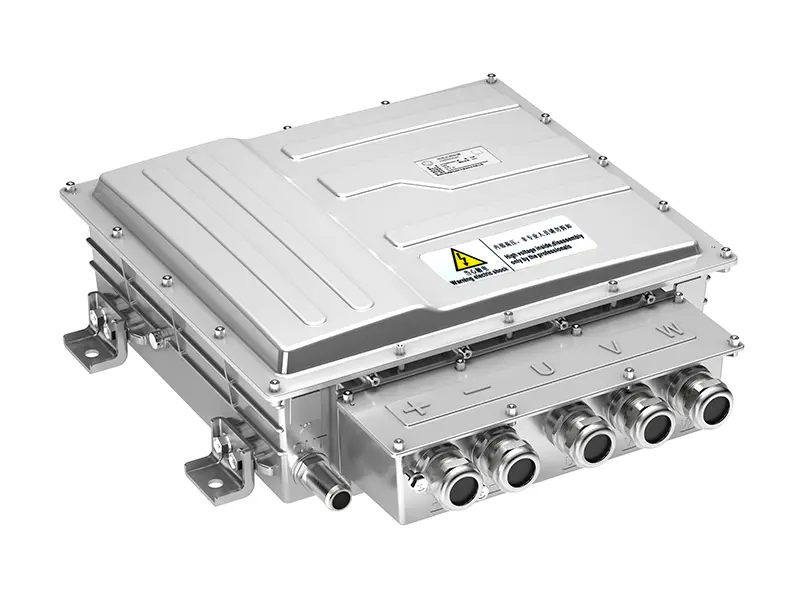
The ev Axle is a cutting-edge component that integrates an electric motor, transmission, and power electronics into a single compact unit. This innovation is transforming how vehicles are propelled by replacing traditional mechanical power transfer mechanisms with more efficient, electronically controlled systems.
To fully appreciate the significance of an ev Axle, it’s essential to first understand the function of a standard axle in a vehicle’s powertrain.
The Role of a Traditional Axle
A traditional axle is a fundamental part of a vehicle’s drivetrain, responsible for:
- Supporting the chassis and vehicle weight – Axles bear the structural load of the vehicle.
- Transmitting power to the wheels – They transfer torque from the engine or electric motor to propel the vehicle forward.
A standard powertrain consists of:
- An engine (internal combustion or electric motor) – The primary source of power.
- A transmission – Converts and optimizes power delivery.
- A driveshaft – Transfers rotational energy.
- A differential – Distributes power between wheels.
- Axles – Deliver power directly to the wheels.
Historically, axles were simple rods with wheels attached, but modern axles incorporate advanced mechanisms to enhance control, efficiency, and stability.
The Evolution from Traditional Axles to ev Axles
In recent years, manufacturers have begun integrating axles with electric drive systems, creating the ev Axle—a more efficient, streamlined solution for electric and hybrid vehicles.
An ev Axle combines:
- An electric motor – Replaces the internal combustion engine.
- Transmission gearing – Designed to handle high torque and regenerative braking.
- Power electronics – Controls energy flow and efficiency.
This integration eliminates the need for multiple drivetrain components, reducing vehicle weight and improving overall efficiency.
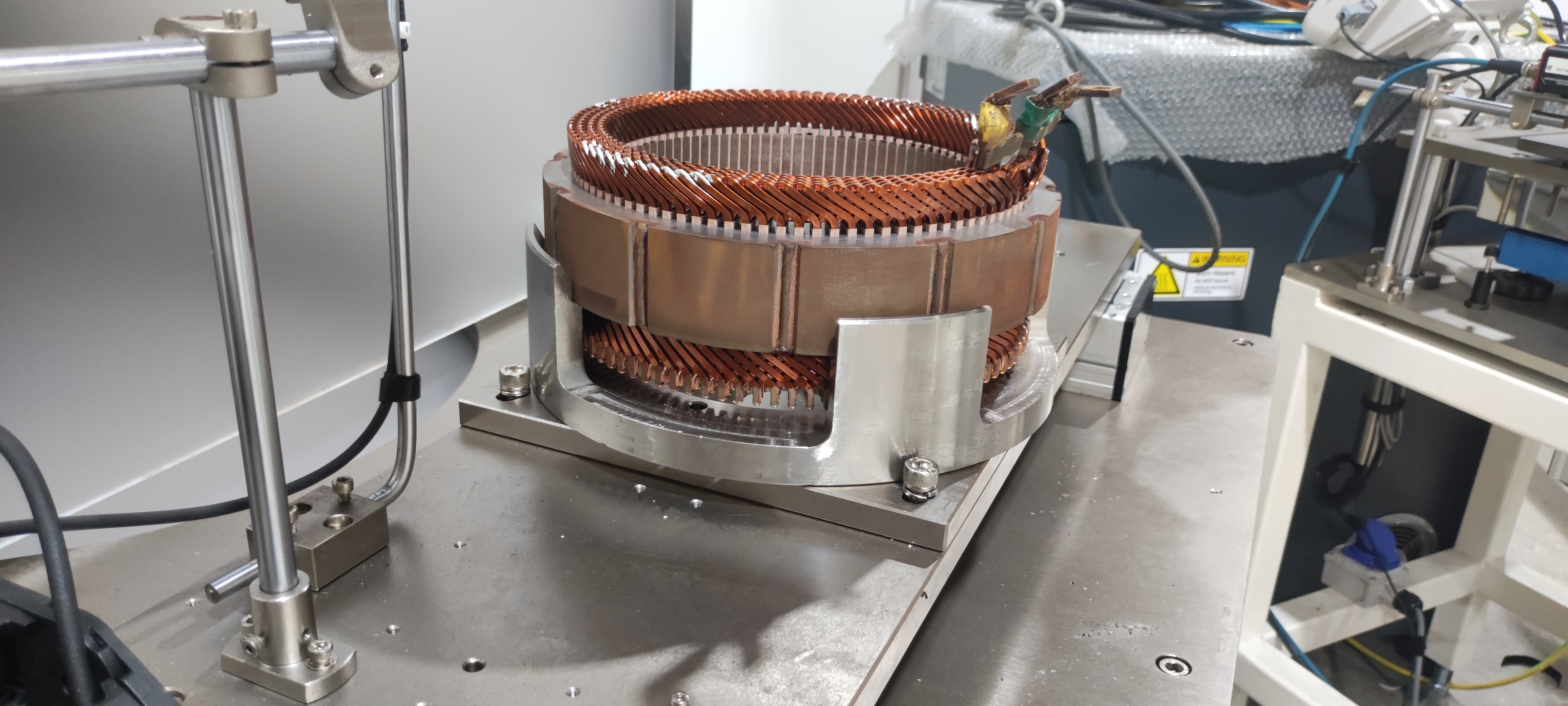
How ev Axles Work
Powering an ev Axle
Ev Axles derive energy from battery-powered electric motors, typically using lithium-ion (Li-ion) batteries. The size and configuration of an ev Axle depend on the vehicle’s design and power requirements.
- Single-motor ev Axles – Suitable for smaller vehicles and light-duty applications.
- Dual-motor ev Axles – Used in larger vehicles requiring additional power and torque.
The latest ev Axles feature integrated motor and transmission systems, reducing weight and complexity while enhancing efficiency.
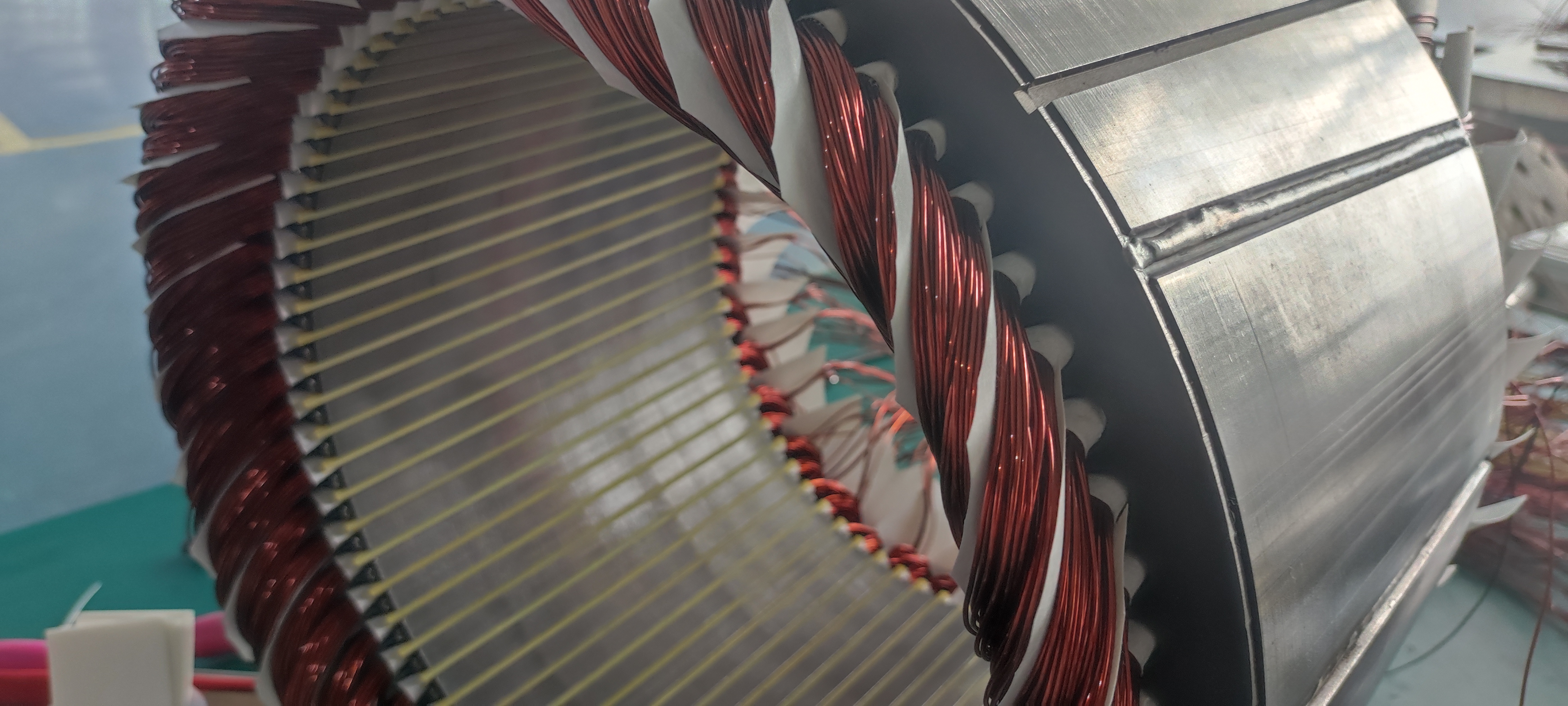
Types of Motors Used in ev Axles
Different types of electric motors can power ev Axles, each offering distinct advantages:
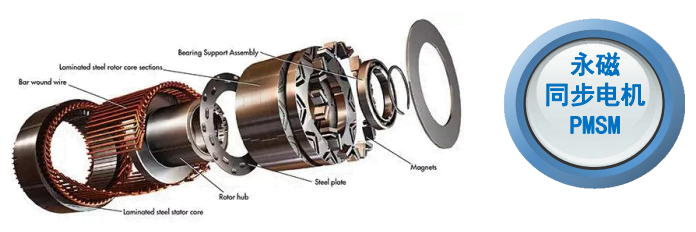
Permanent Magnet Synchronous Motor (PMSM)
High power density and efficiency.
Ideal for performance-oriented applications.
Induction Motor (IM)
Lower cost and durable.
Less efficient than PMSM.
Switched Reluctance Motor (SRM)
Cost-effective and simple.
Limited torque capacity.
Fuel Cells as an Alternative Power Source
Apart from batteries, hydrogen fuel cells can also power ev Axles.
A fuel cell converts hydrogen into electricity, producing only water and heat as emissions.
Hydrogen fuel cells offer longer range and faster refueling compared to batteries.
Infrastructure challenges currently limit widespread adoption, but hydrogen-powered vehicles are expected to become more viable by 2030.

The benefits behind ev Axle
Ev Axles offer several compelling advantages that make them a crucial component in modern electric and hybrid vehicles:
1. Improved Vehicle Efficiency
Reduces energy loss by eliminating mechanical power transmission inefficiencies.
Enhances regenerative braking, which helps recharge the battery while slowing down.
2. Increased Cargo Capacity
Lighter design allows vehicles to carry more payload.
Frees up space for additional batteries, extending vehicle range.
3. Lower Maintenance Costs
Fewer moving parts reduce wear and tear.
Simplifies drivetrain architecture, decreasing maintenance complexity.
4. Quieter and Smoother Ride
Eliminates engine noise associated with combustion engines.
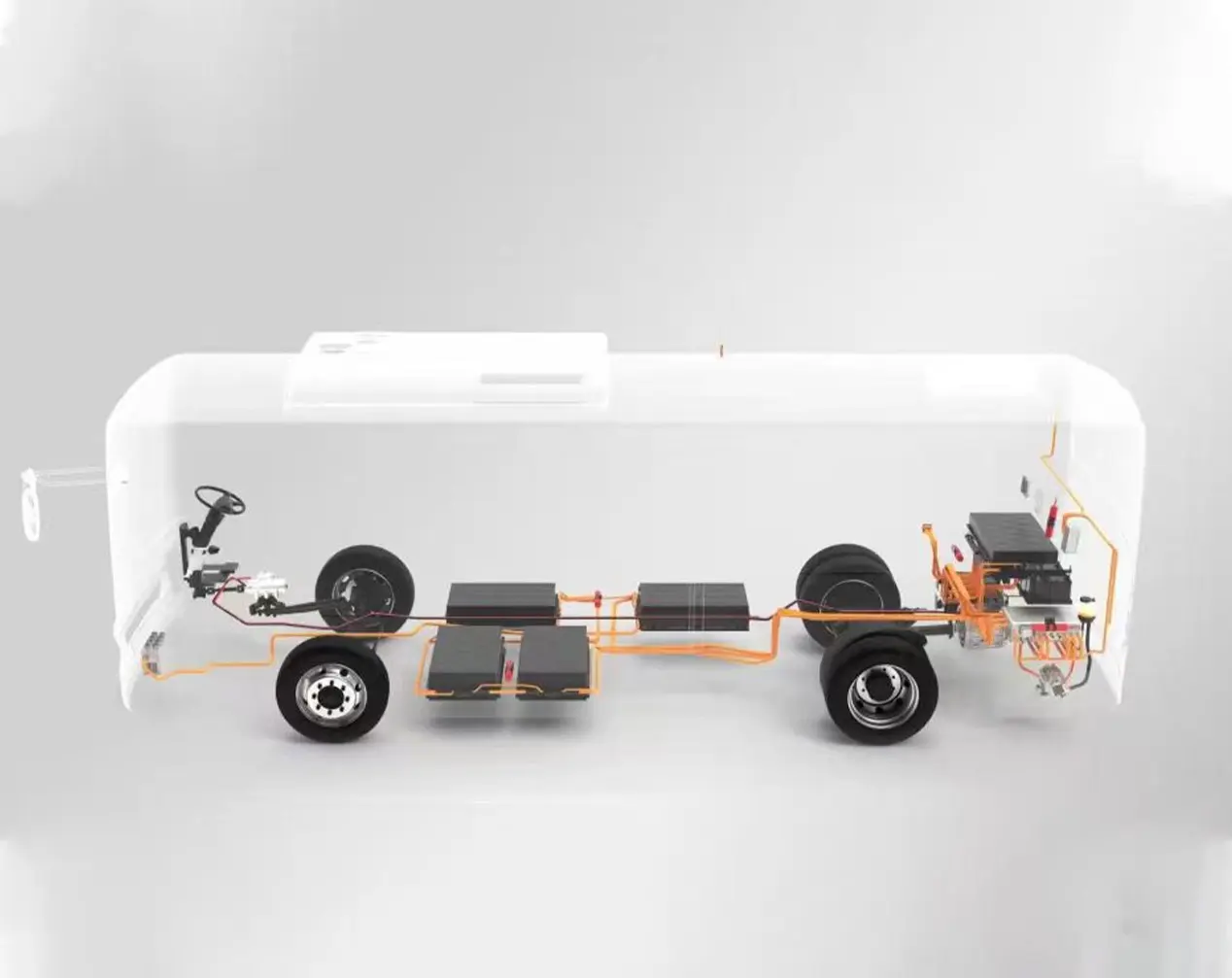
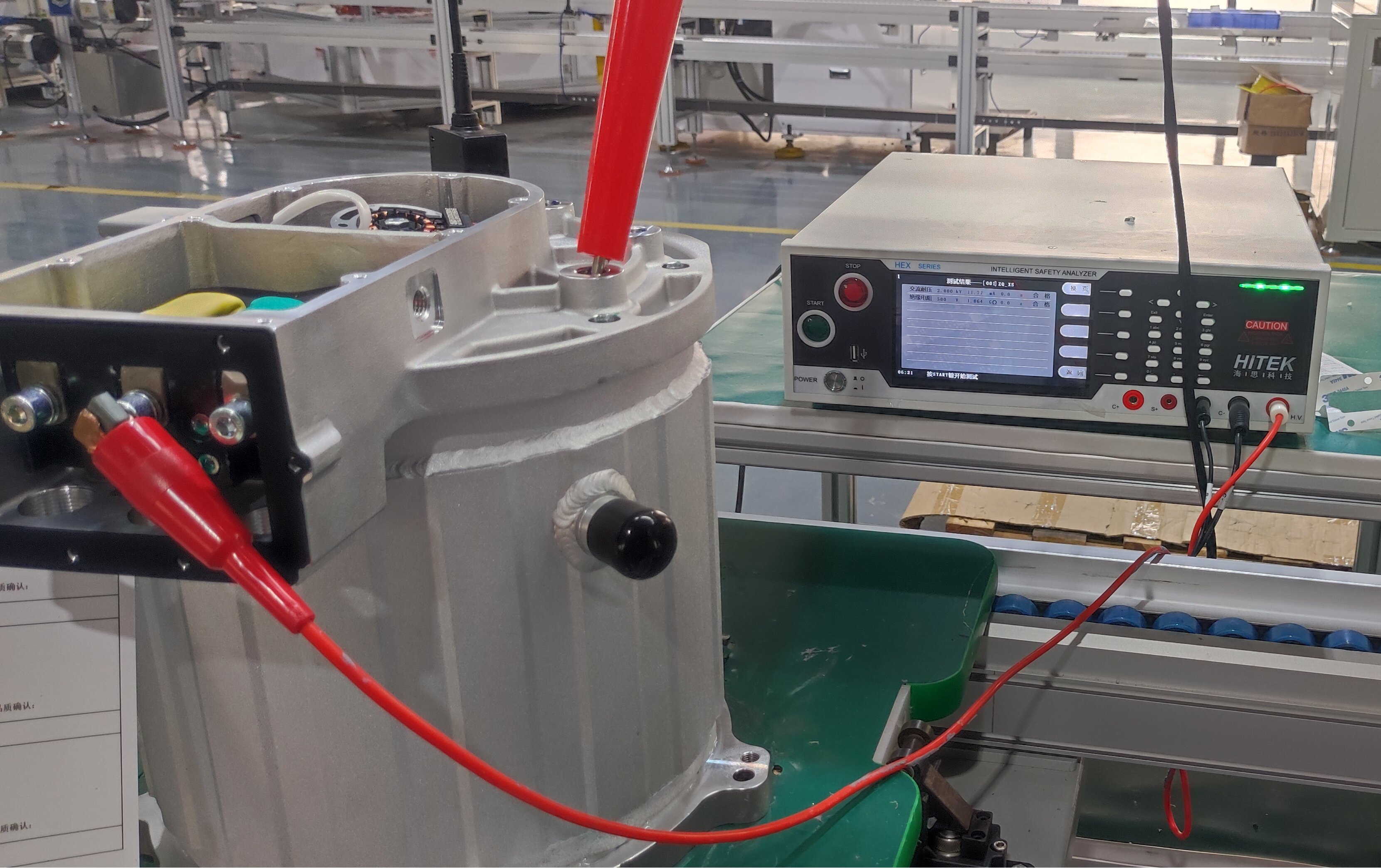
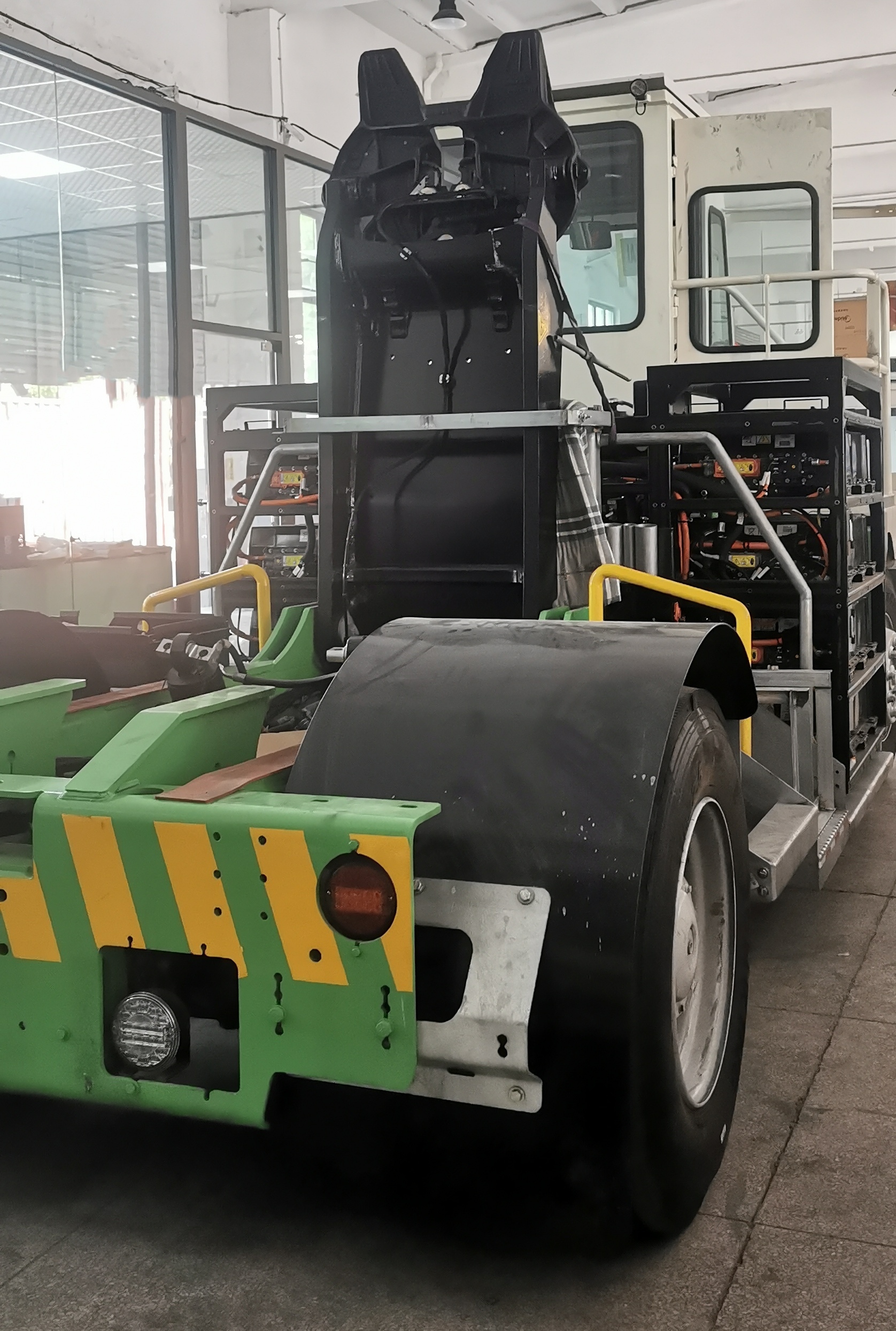
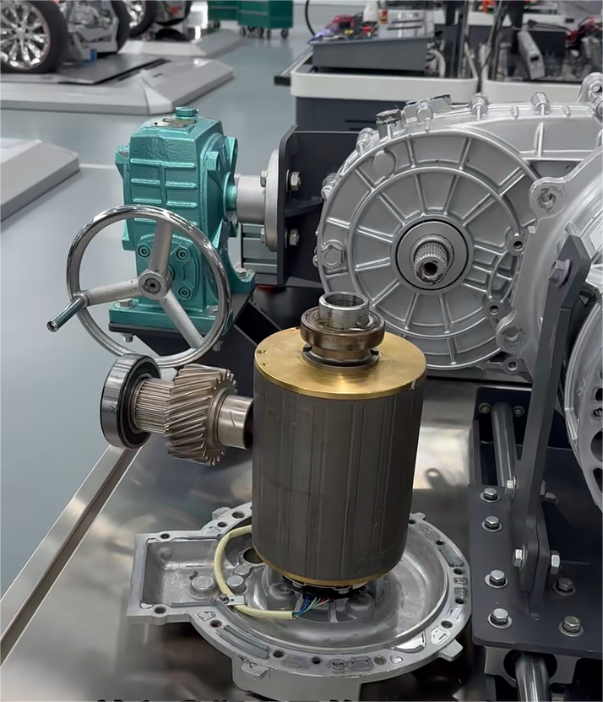
When it comes to the pure EV truck, understanding the differences between traditional electric motor structures and modern e-axle systems is crucial. Let’s use an electric dump truck as an example to explore these differences.
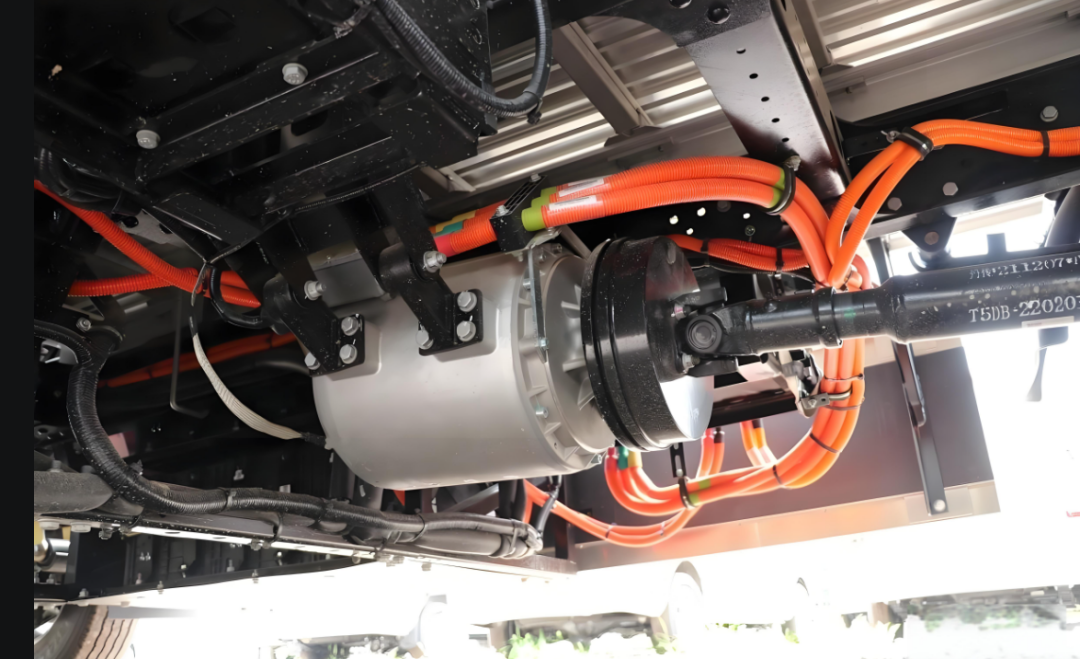
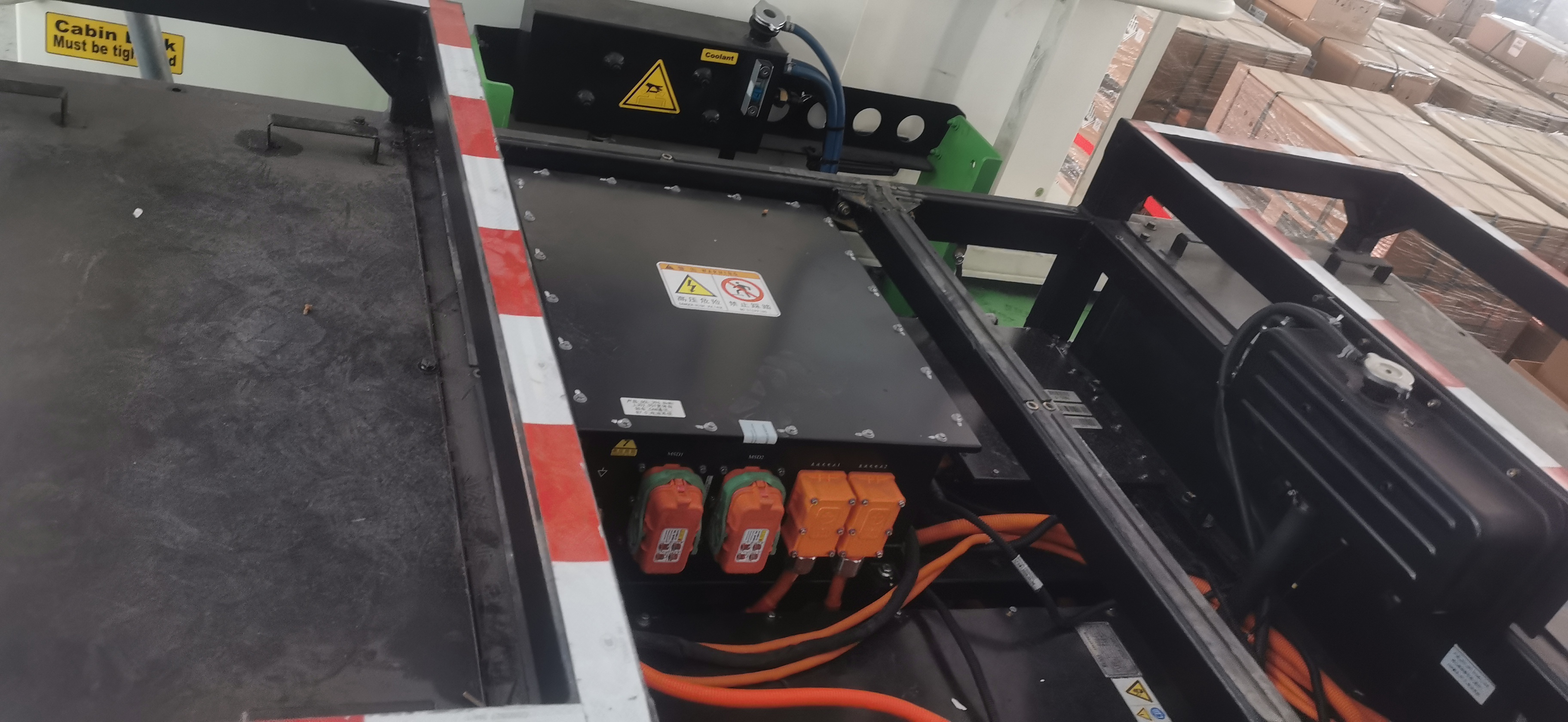
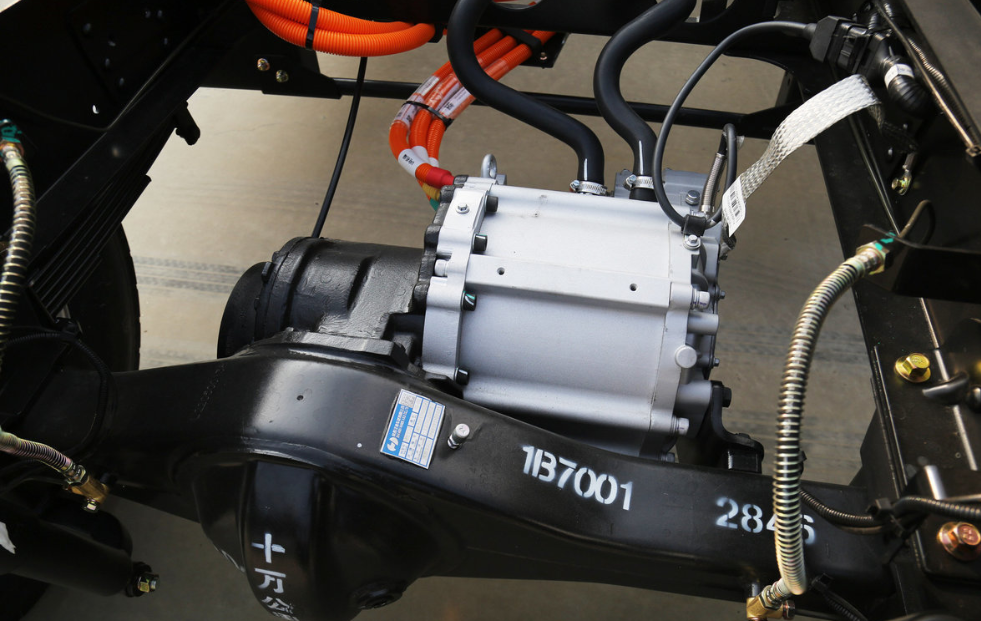
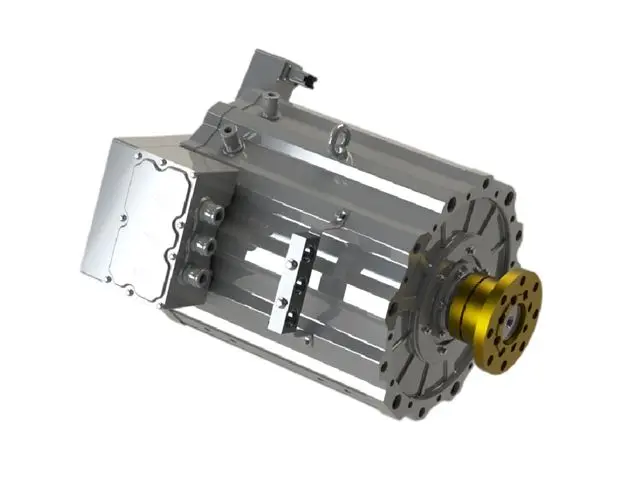
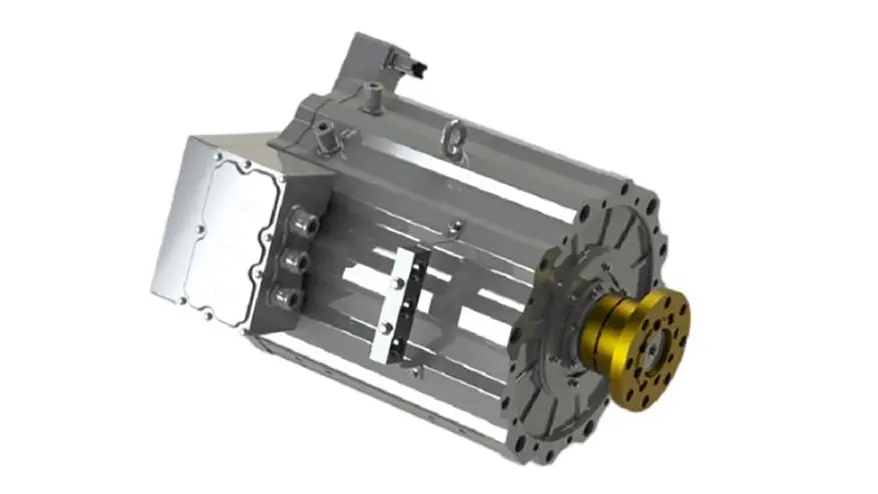
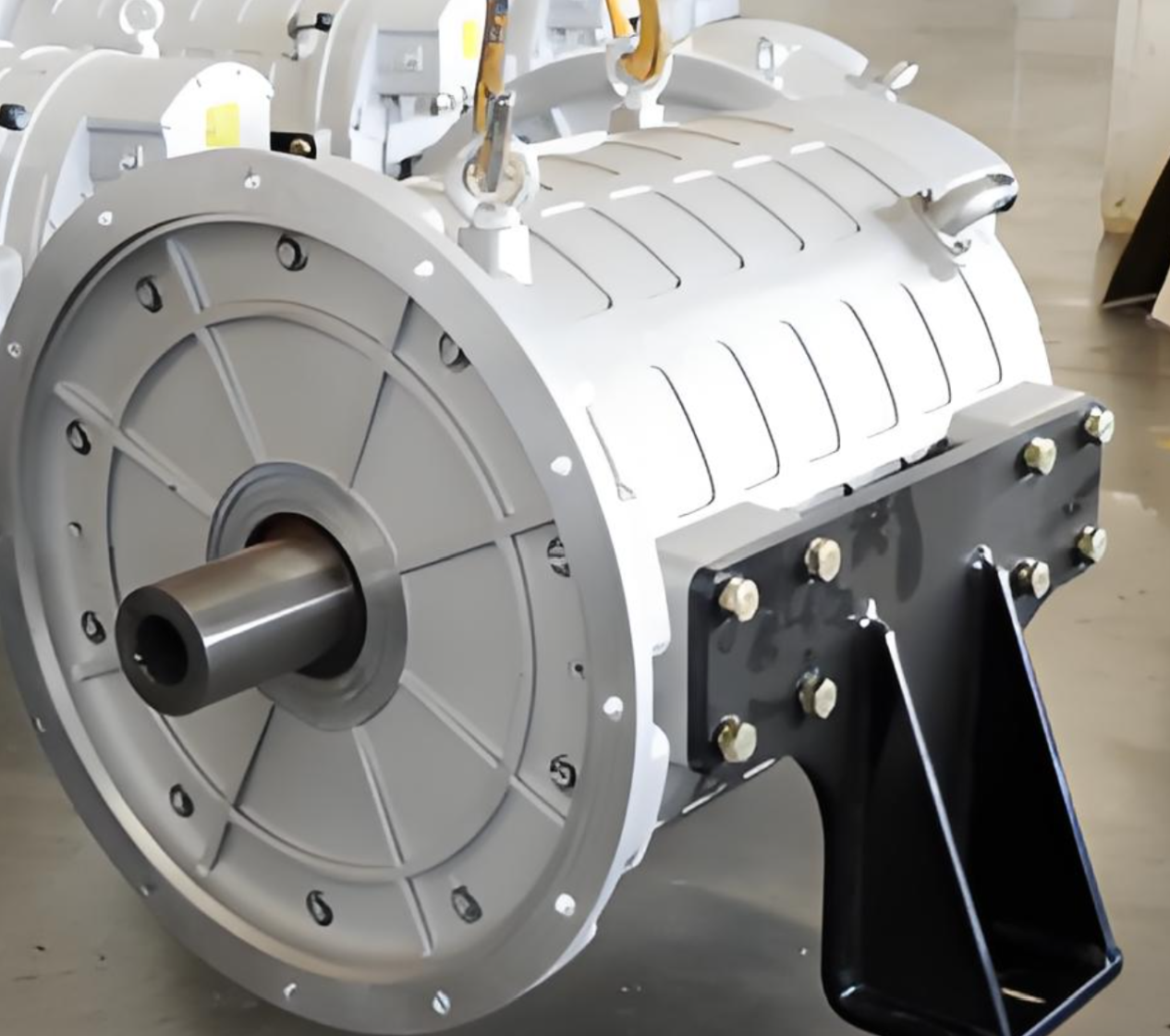
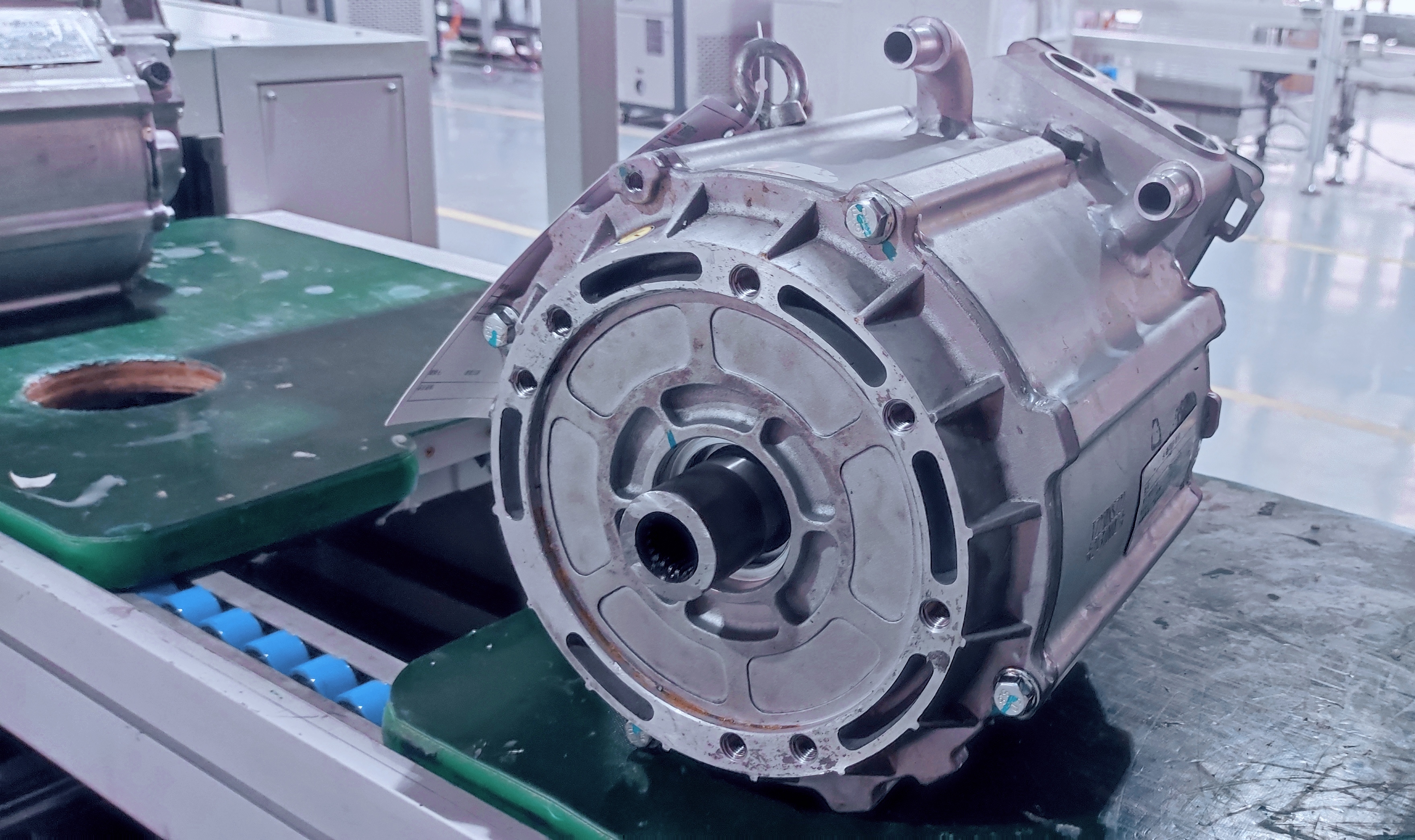
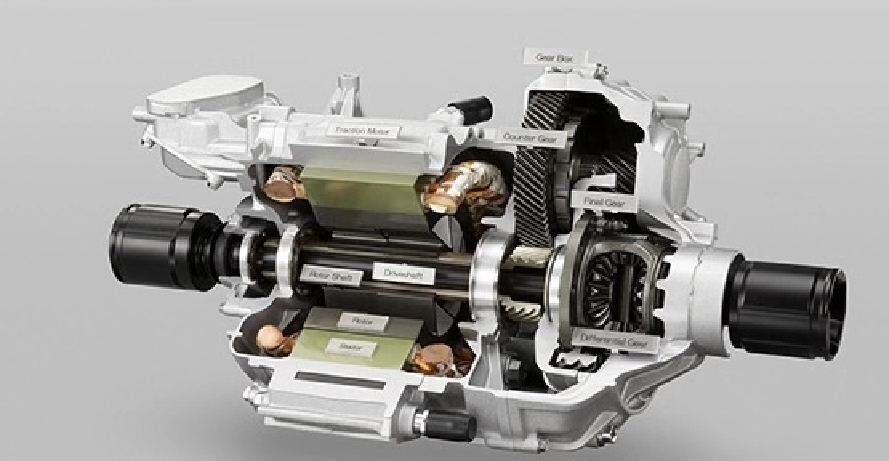
Traditional Drivetrain Structure – Direct Drive Motor
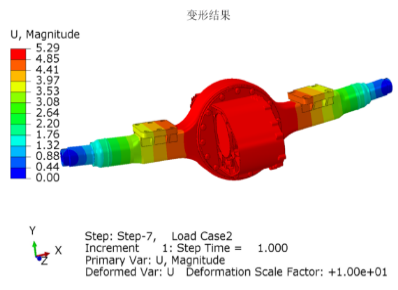
The drivetrain in electric trucks closely mirrors the configuration of conventional vehicles. At the core of this system is the drive motor, which serves the same role as a diesel engine. Positioned directly behind the motor is a reducer, functioning similarly to a conventional gearbox. Its primary function is to enhance torque by lowering the motor’s speed, thereby increasing power output. This boosted power is then delivered via a driveshaft to the rear axle. With a gear ratio of approximately 5.857, the rear axle operates similarly to those found in traditional dump trucks.
How It Works
- Motor Output: The electric motor generates high-speed, low-torque power.
- Torque Amplification: The reducer utilizes gears to decrease speed while significantly increasing torque.
- Power Transmission: The enhanced torque is transferred through the driveshaft to the rear axle.
- Final Drive: The rear axle further boosts the torque before delivering it to the wheels, driving the truck forward.
A key feature of this system is the two-speed capability of the reducer, enabling the vehicle to switch between different gear ratios depending on the load. This functionality, similar to gear shifting in a traditional transmission, ensures an optimal balance between speed and power.
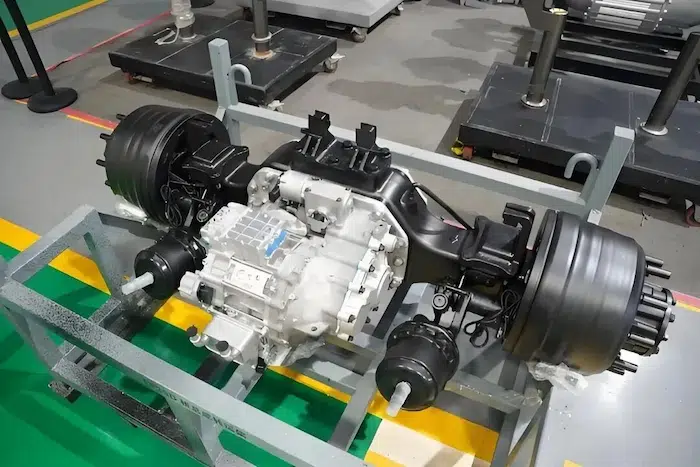
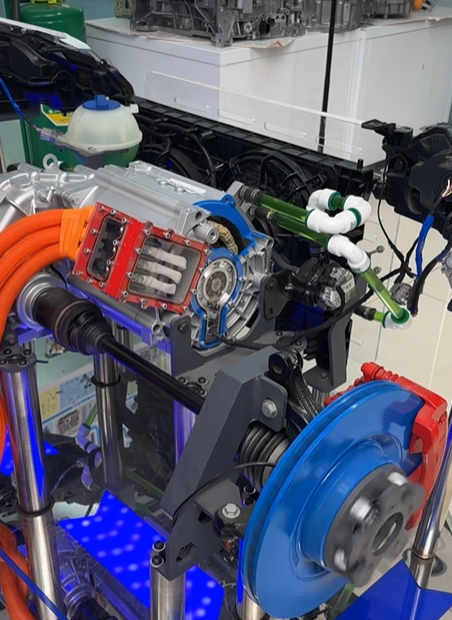
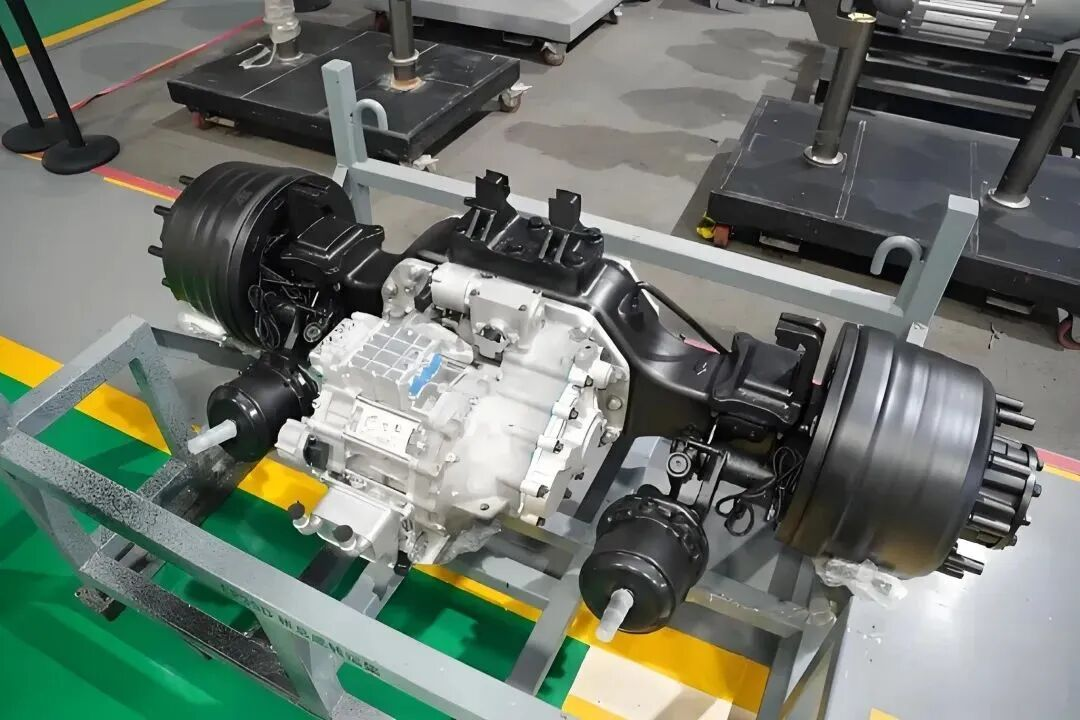
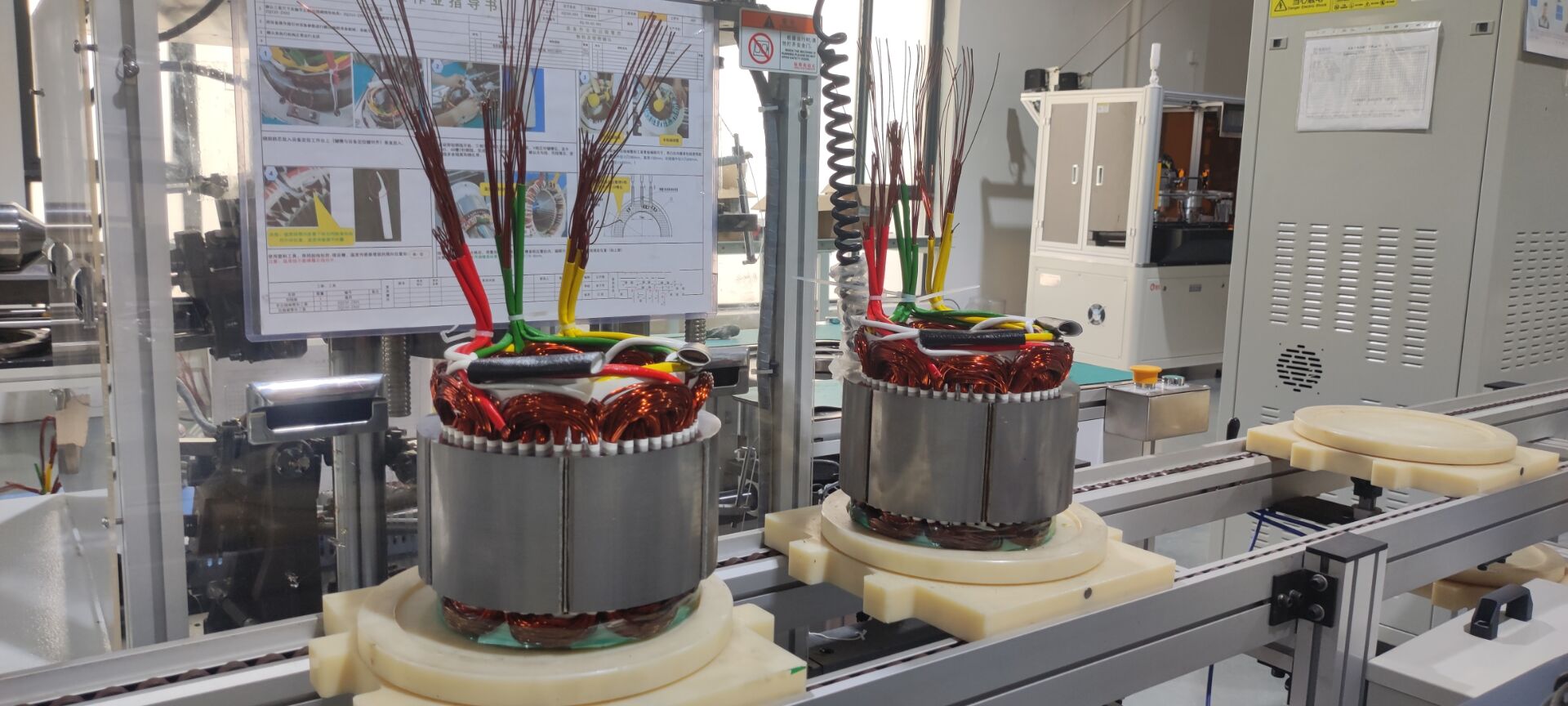
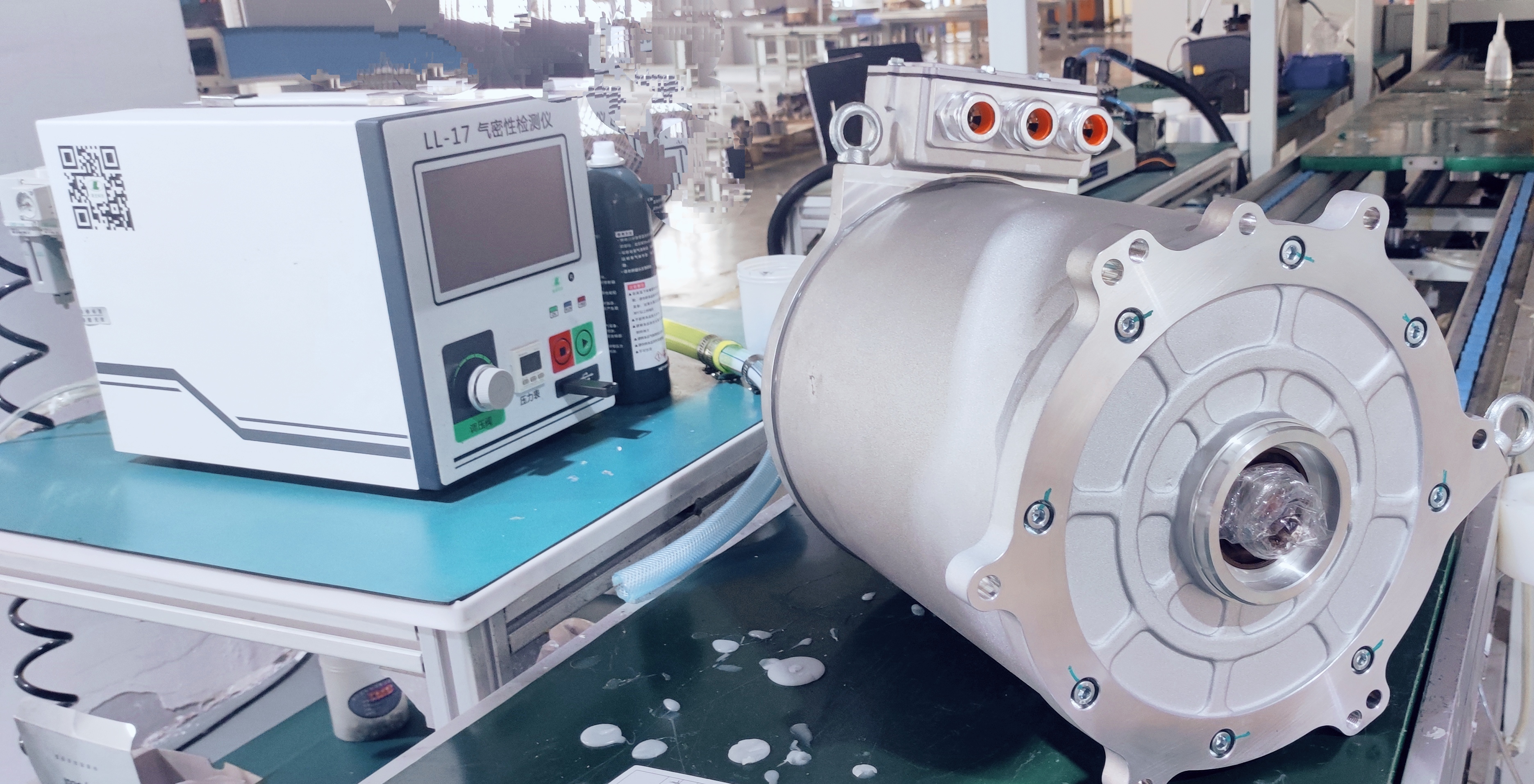
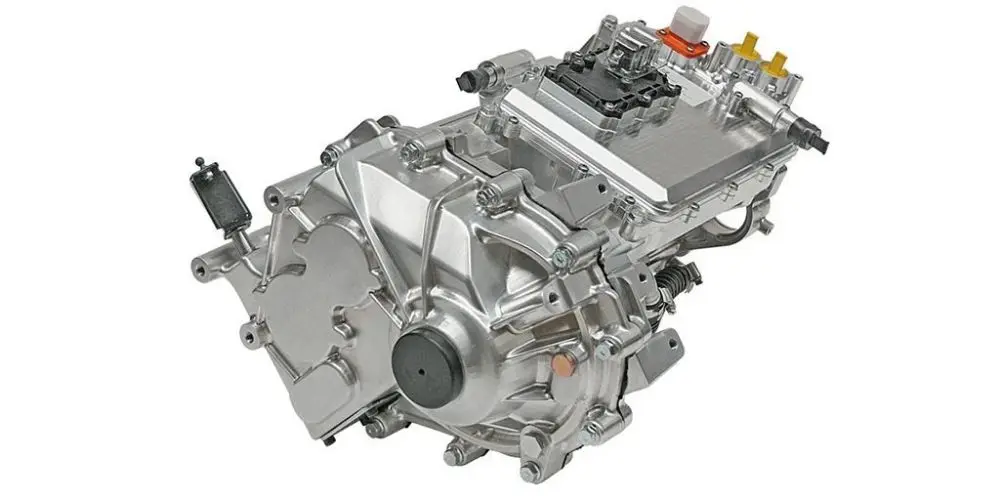
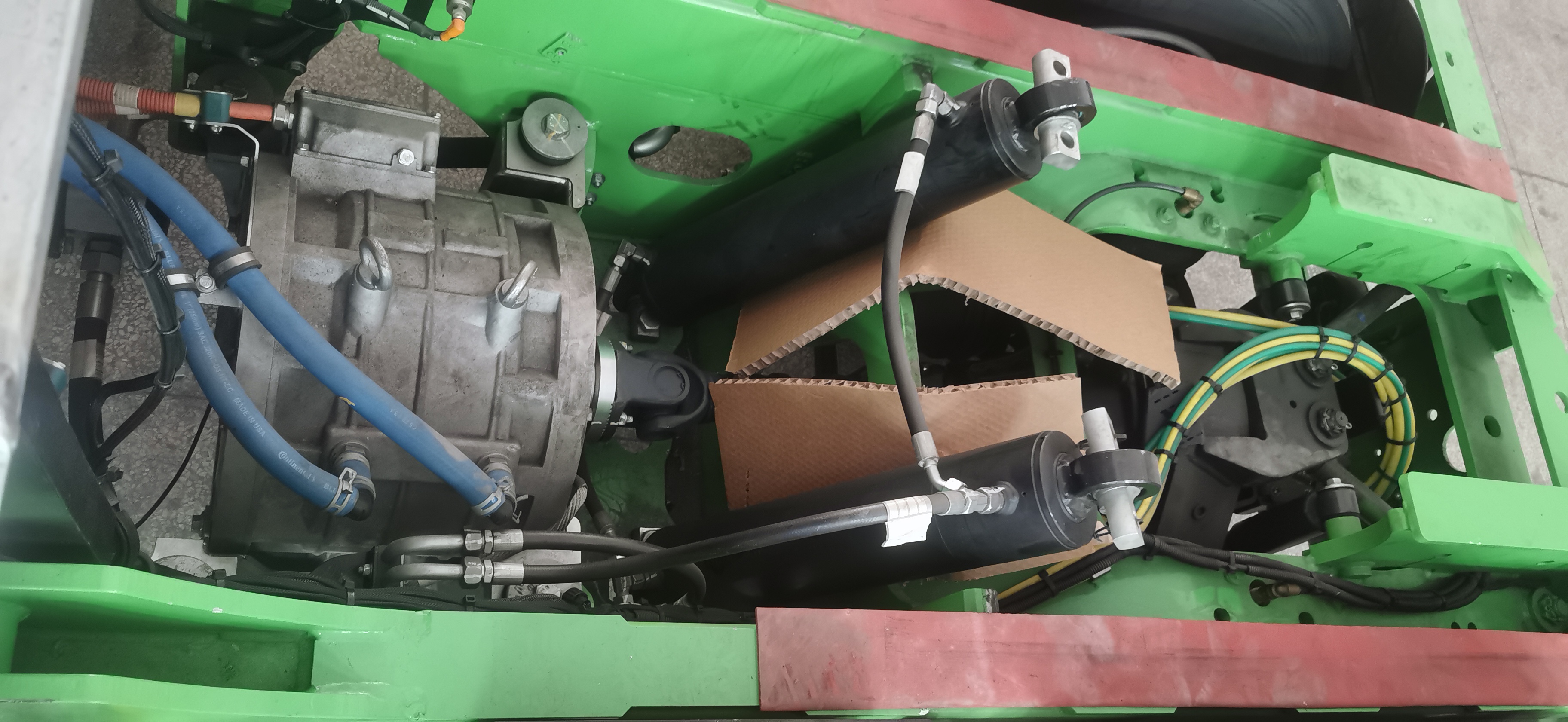
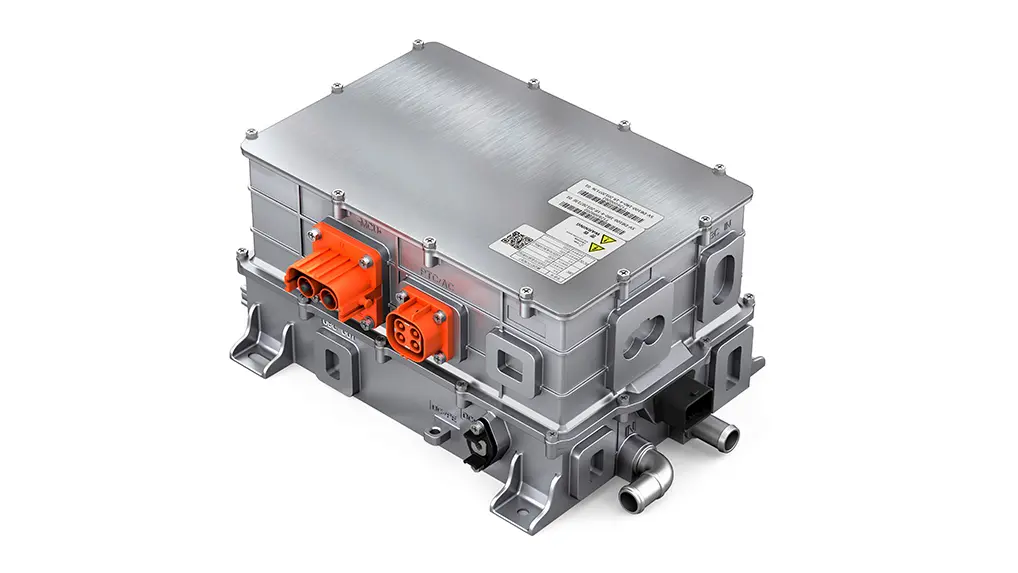
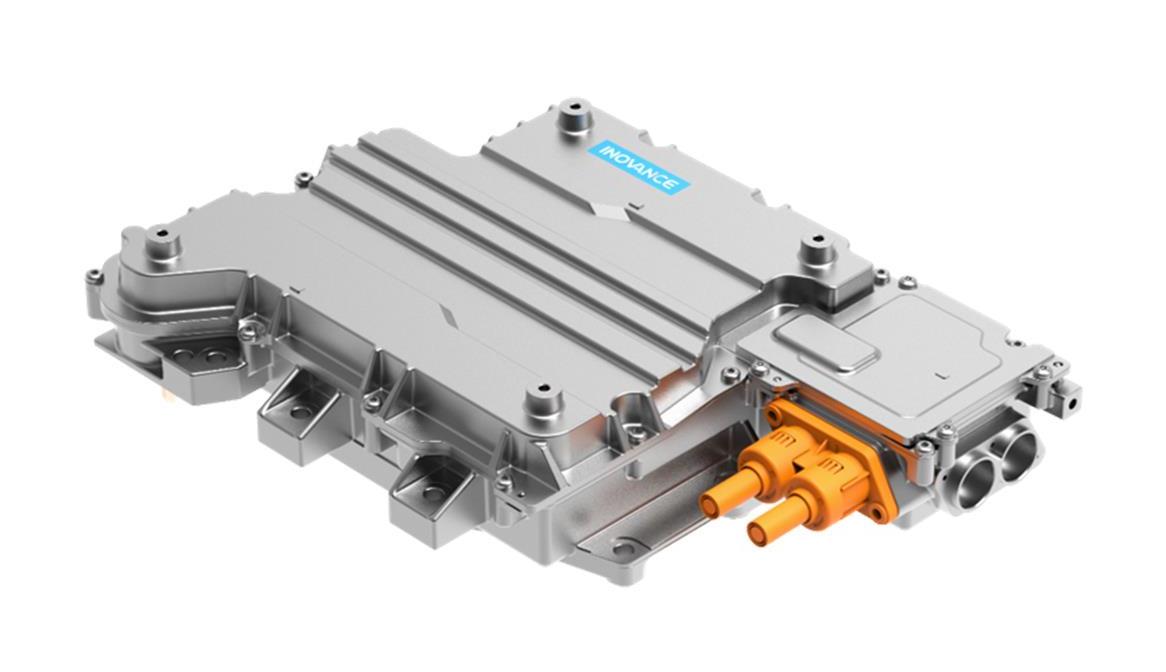
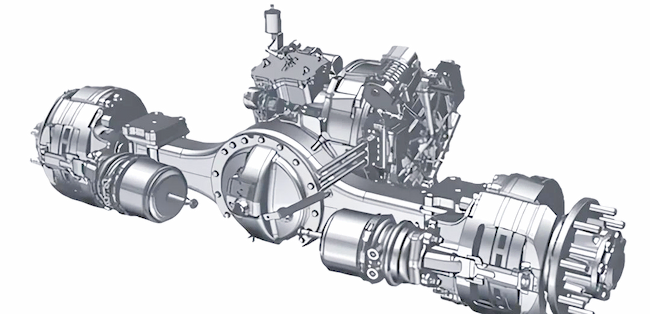
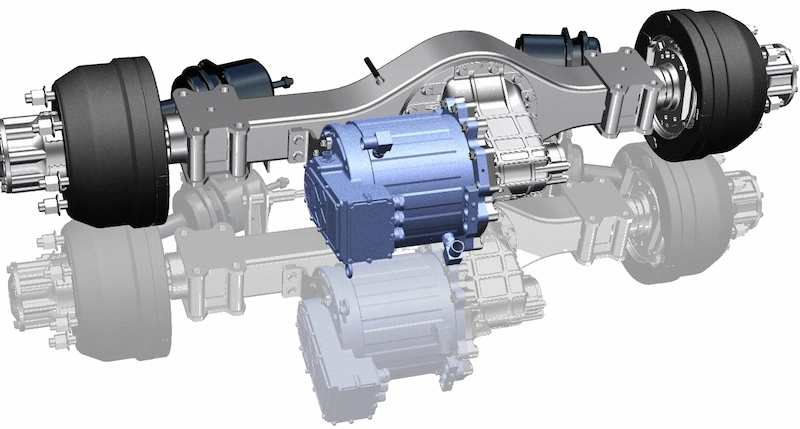
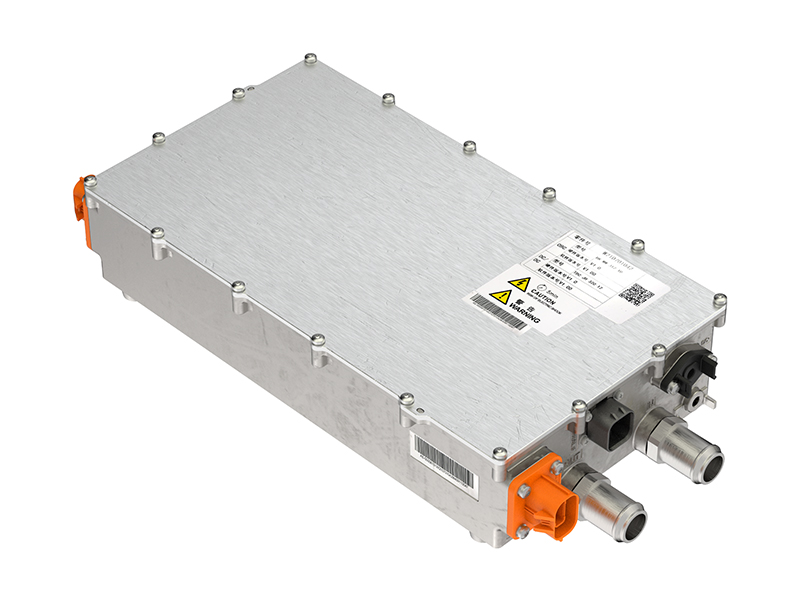
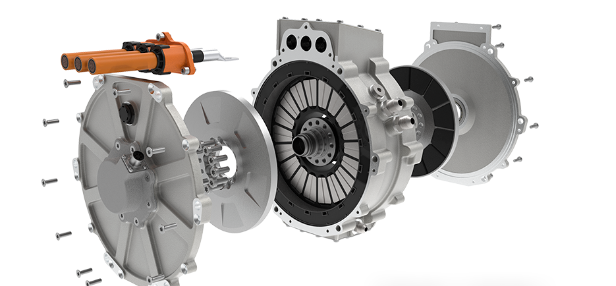
E-Axle System
Now, let’s explore the e-axle system, a technology that integrates the electric motor directly with the rear axle. This system combines four essential components into a single unit: the motor, rear axle, transmission, and differential. This streamlined design offers several key advantages:
- Reduced Weight: By eliminating the need for a separate reducer and driveshaft, the e-axle lowers the vehicle’s overall weight, allowing for a higher cargo capacity.
- Enhanced Energy Efficiency: Directly driving the rear axle minimizes power loss typically associated with traditional drivetrains, improving transmission efficiency and extending the truck’s range by approximately 20 kilometers per charge.
- Greater Space Optimization: Removing components like the motor, driveshaft, and gearbox frees up chassis space, making room for additional batteries and further increasing the vehicle’s driving range.
- Simplified Design and Improved Reliability: With fewer moving parts and a more compact structure, the e-axle reduces mechanical complexity, leading to fewer potential failure points and greater reliability.
However, the e-axle system also presents challenges. Integrating the motor directly with the rear axle limits space for torque amplification mechanisms, which may restrict power output compared to traditional systems with a gearbox. To achieve high performance levels, e-axle designs must incorporate advanced engineering solutions to compensate for this limitation.
Conclusion
The evolution of electric truck drivetrains highlights the shift from traditional motor-reducer setups to integrated e-axle systems, each offering distinct advantages and challenges. While the conventional drivetrain mirrors that of diesel-powered trucks, using a reducer and driveshaft to amplify and transmit power, the e-axle system streamlines efficiency by integrating multiple components into a single unit.
By eliminating unnecessary mechanical parts, e-axles reduce weight, enhance energy efficiency, and free up valuable chassis space, ultimately leading to improved range and reliability. However, their design limitations in torque amplification require innovative engineering to match the power output of traditional setups.
As electric truck technology continues to advance, the adoption of e-axle systems is expected to grow, driven by their potential to enhance performance, optimize energy use, and support the transition to more sustainable transportation solutions. Future developments in motor efficiency, battery technology, and drivetrain design will be crucial in shaping the next generation of electric trucks, ensuring they meet the increasing demands of modern logistics and freight transport.
Read More: China’s DeepSeek Has Given AI Startups A Lesson That Automakers Learned Years Ago.